
The e-book provided discusses key considerations and best practices for conducting accurate and reproducible quantitative PCR (qPCR) experiments, particularly in the context of gene expression analysis. Here’s a summary of the main points:
Types of Assay Controls in qPCR:
To ensure reliable results in qPCR experiments, several controls are essential:
- DNA Contamination Control Assay:
- Detects genomic DNA (gDNA) contamination in RNA samples.
- Important for assessing potential interference in PCR reactions.
- Positive PCR Control Assay:
- Verifies the overall performance of the PCR reaction with a sample.
- Useful for comparing PCR performance across different samples.
- RNA Quality Assay:
- Assesses RNA integrity and whether degraded RNA might affect the PCR results.
- Compares RNA quality across samples to understand potential impacts on results.
- Reverse Transcription Control Assay:
- Validates the reverse transcription (RT) process, ensuring efficient cDNA synthesis.
- Enables comparison of RT efficiency across different samples.
- No-Template Control:
- Ensures there is no contamination in the reagents used for PCR (e.g., primers or water).
Reference Genes for Normalization:
In gene expression analysis, reference genes are used to normalize qPCR data to account for variations in RNA quantity, integrity, or cDNA loading. The following steps should be taken to ensure the accuracy of reference gene selection:
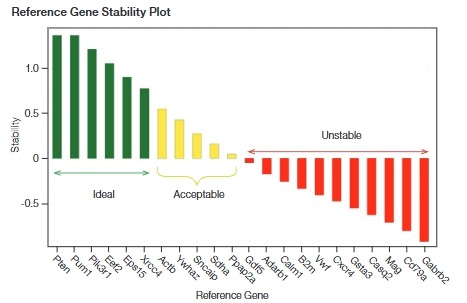
- Choose Candidate Reference Genes: At least five candidate genes should be evaluated.
- Sample Selection: Select representative samples from the experimental groups.
- RNA Preparation: Normalize RNA concentration and ensure consistent sample preparation across conditions.
- Reverse Transcription: Use a standardized reverse transcription protocol.
- Gene Expression Analysis: Perform qPCR with both the target genes and candidate reference genes.
- Evaluate Stability: Analyze the stability of candidate reference genes using tools like CFX Maestro Software or other external tools like NormFinder and geNorm.
The most stable reference genes are categorized as “Ideal,” which exhibit minimal variation across conditions. Unstable genes should be avoided as they can introduce inaccuracies into the normalization process.
Housekeeping Genes as Poor Reference Genes:
Housekeeping genes such as GAPD and ACTB have historically been used for normalization, but they are often unsuitable due to:
- Variable expression across different experimental conditions.
- Regulation by experimental conditions, which could affect the reliability of the normalization.
- Cell-type specific expression, which may not be consistent across different tissues or experimental conditions.
- Stress responses that might cause upregulation or downregulation, potentially skewing results.
Stability Plot for Reference Gene Validation:
Using a stability plot (such as the one shown in the document), researchers can evaluate and select the most stable reference genes for their experimental conditions. These plots compare the expression stability of different genes across experimental conditions.
Conclusion:
Accurate normalization using stable reference genes is crucial for obtaining reliable qPCR results. Employing appropriate assay controls (DNA contamination, positive PCR, RNA quality, reverse transcription) ensures that qPCR data is robust and reproducible. Proper validation of reference genes using a systematic approach and tools like CFX Maestro Software can greatly enhance the reliability of gene expression studies.
References:
- Key studies and tools referenced for qPCR validation and reference gene selection include works by Vandesompele et al. (2002) and Song et al. (2022).
By following these best practices, researchers can ensure the consistency and accuracy of their gene expression analysis results.
This article is posted at bio-rad.com

Please fill out the form to access the content






